In a recent publication in the Journal of Biomedical Semantics, researchers from the Erasmus University Medical Center (EMC) in Rotterdam have presented a machine learning (ML) model that predicts with 78% accuracy whether a drug is efficacious for a disease. This represents an improvement of more than 10 percentage points from earlier scientific, peer reviewed models; a very significant step forward.
The researchers worked closely together with Euretos and extracted 1.58 million protein relations involving 15,124 individual proteins from the Euretos AI Platform. For each protein the associations with diseases and drugs were added and to create disease and drug related protein interaction networks. The machine learning model then analysed the relatedness between drug protein networks and disease protein networks to make the drug-disease efficacy prediction. One of the key benefits the Euretos AI Platform provides was to also included indirect relations between these networks.
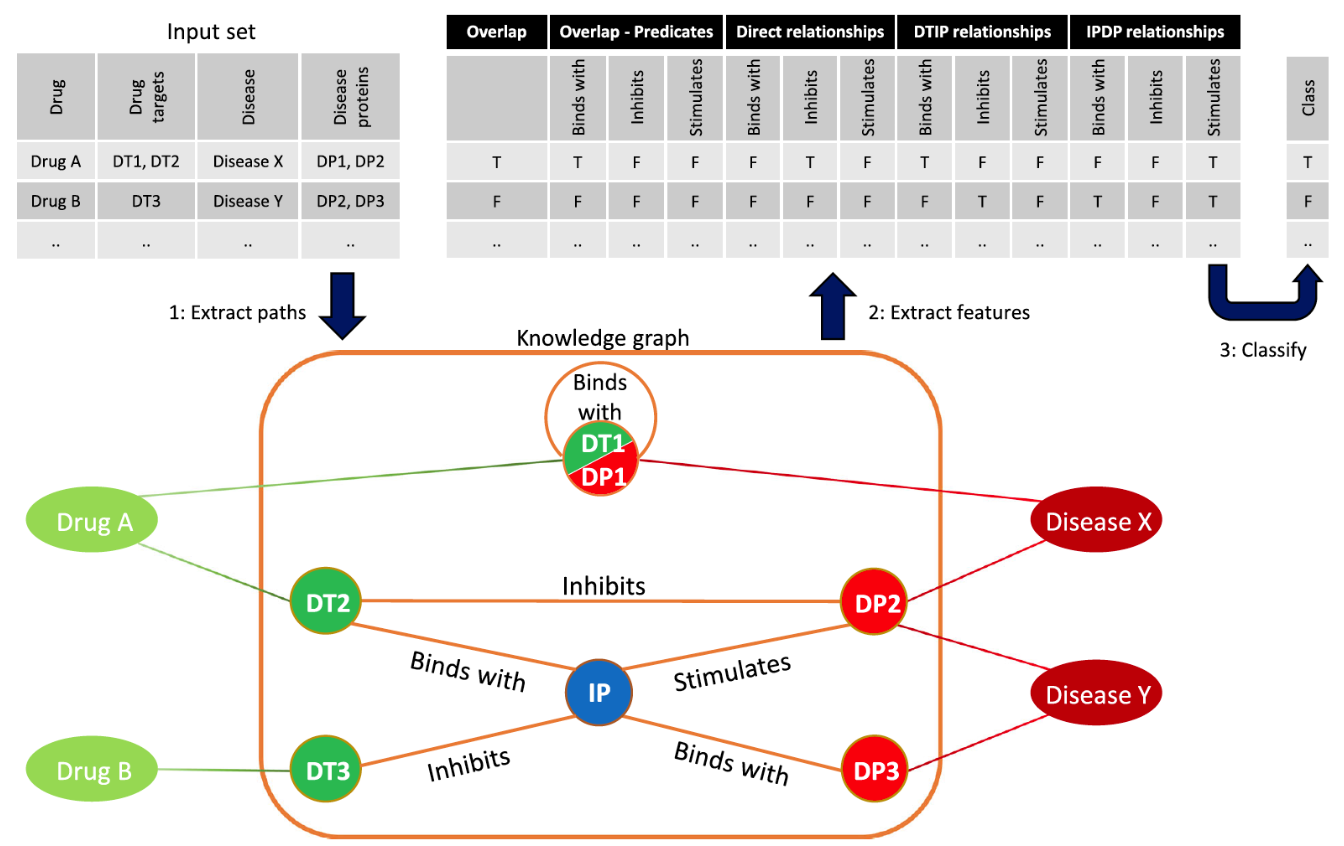
The approach taken can be summarised as follows:
This paper highlights three key value adds of the Euretos AI Platform.
First of all, the granular relation types and integrated references of the Euretos AI Platform add significant value to computational methods, such as machine learning.
Although a relatedness analysis based on drug and disease protein networks has been done before, the Euretos AI Platform enabled the researchers to, for the first time ever, add relation types and ‘provenance’ (sources) of the relations. In total 45 different types of relations were used. Both predicate features and provenance features substantially improved performance to 78,1% as compared to 65,6% in the then state-of-the-art ML model.
Secondly, using the pre-integrated data from 250+ datasources of the Euretos saves a very significant amount of time on data integration.
For the project, the extracted protein relations came from 25 different knowledge sources. Integrating these sources would take a very significant amount of effort, which can be better spent at developing smart computational approaches. As the researchers state: “We performed our analysis on an existing, commercially available knowledge graph, saving us the considerable amount of time and effort required to integrate the knowledge sources with each other.”
Thirdly, data integration in the Euretos AI Platform enables indirect relations between concepts, in this case drugs and diseases, to be leveraged with great effect.
In the project drug targets and disease proteins were connected by 267,032 direct relations, and almost 50 million indirect (two-step) paths. One of the findings of the research is that the ML model performs well even if direct relations are not included in the analysis: “Removal of the overlap and direct relationship features, which included the four most important ones, showed that our method can still be used when only indirect paths are available. A lack of proximity between drug targets and disease proteins can therefore be compensated with predicate and provenance information.”
As this publication highlights, the semantically integrated data within the Euretos AI Platform is ready to use, very powerful and has significant impact on outcomes of computational methods.
Subscribe to our mailing list and receive our quarterly updates!
Read our Terms and Conditions

Keep up with our latest news and events. Sign up for our newsletter.