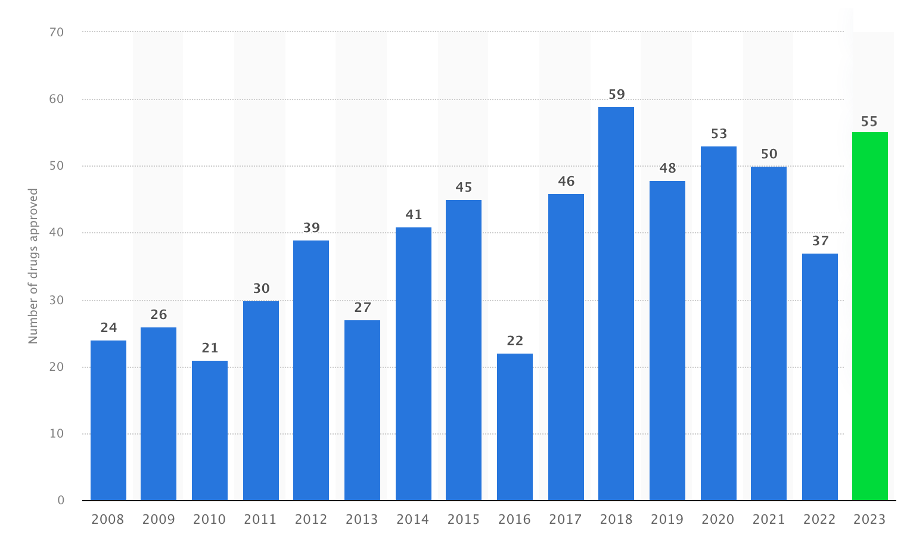
The year 2023 has been a great year in drug development with 55 new drugs reaching FDA approval; the second highest number in over 30 years. What sets 2023 apart is not just the number of drugs approved but the diversity and innovation they represent. We saw significant strides in areas like oncology, CNS disorders, and rare diseases. A common theme in all these cases are the critical roles played by both basic and translational research.
Basic research, often conducted without immediate applications in mind, has always been the bedrock of biomedical innovation. It's at this stage that the mysteries of biology and disease are unraveled. The discoveries made in this phase – be it understanding genetic mutations, cellular pathways, or the immunology of diseases – set the stage for future therapeutic interventions. The 2023 drug approval of "Sohonos" which is the first and only treatment for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva – a rare and debilitating condition, is a good example of this. The development of this novel drug can be traced back to fundamental research on bone development and pathological ossification. This exemplifies how explorations driven by sheer curiosity can eventually lead to therapeutic marvels.

Translational research, the bridge between the laboratory and the clinic, is where the potential of basic research is actualized into real-world medical solutions. It's a domain that transforms theoretical knowledge into drugs, vaccines, or diagnostic tools. In 2023, this was exemplified by the approval of "Fabhalta" for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. The journey of this drug, from understanding the disease's pathophysiology in a lab to developing a targeted therapeutic strategy, is a case in point of translational research in action. Another example is "Loqtorzi" for nasopharyngeal carcinoma a next-generation PD-L1 and PD-L2 blocker. The approvals of "Pombiliti" for Pompe disease and "Veopoz" for CHAPLE disease are testaments to how translational research has revolutionized treatment options for rare, previously untreatable conditions.
These developments mirror advances in data-driven research technologies, where fundamental research has led to breakthroughs in AI. Building on these new technologies, we see significant improvements in practical research tools for the biopharma industry driving further innovation in drug development.
It is clear that the journey from a laboratory concept to a lifesaving drug is a collaborative relay race between basic and translational research. Each plays a distinct role, yet their interdependence is undeniable. The success stories of 2023 are therefore a powerful reminder of how basic and translational research both combine experimental science and data-driven research technologies. This synergy is crucial for addressing the complex challenges in drug development, especially in the context of precision medicine and treatment personalization.
As we reflect on 2023, we are thankful that our dedication to data-driven research technology contributes to both the basic and translational research efforts. Euretos’ translational research platform and predictions have already contributed to approved drugs and active clinical trials in oncology, Sjogren's disease, Ulcerative Colitis, NASH and epilepsy with 5 different biopharma clients. For 2024, we look forward to playing our part in the collaborative relay race between basic and translational research, bridging the laboratory, the data-center and the clinic to improve patient outcomes and overall health.
Subscribe to our mailing list and receive our quarterly updates!
Read our Terms and Conditions

Keep up with our latest news and events. Sign up for our newsletter.